This is Part 16 of a 'How-To' effort to compile a list of tools (free and commercial) that can help IT administrators comply with what was formerly known as the "SANS Top 20 Security Controls". It is now known as the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Security Controls. A summary of the previous posts is here:
- Part 1 - we looked at Inventory of Authorized and Unauthorized Devices.
- Part 2 - we looked at Inventory of Authorized and Unauthorized Software.
- Part 3 - we looked at Secure Configurations.
- Part 4 - we looked at Continuous Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation.
- Part 5 - we looked at Malware Defenses.
- Part 6 - we looked at Application Security.
- Part 7 - we looked at Wireless Access Control.
- Part 8/9 – we looked at Data Recovery and Security Training.
- Part 10/11 - we looked at Secure Configurations for Network Devices such as Firewalls, Routers, and Switches and Limitation and Control of Network Ports, Protocols, and Services.
- Part 12 - we looked at Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges.
- Part 13 - we looked at Boundary Defense.
- Part 14 - we looked at Maintenance, Monitoring, and Analysis of Audit Logs.
- Part 15 - we looked at Controlled Access Based on the Need to Know.
Now we are taking on Account Monitoring and Control.
16-1 - Review all system accounts and disable any account that cannot be associated with a business process and owner.
Free Tools
- AD Info Free - Set very specific filters for AD objects, and report on them in amazing detail.
- Event Logs - If you want to pass event logs off to a SIEM
- Linux User Account Auditing - Blog article filled with great information. Don't forget to read the comments, a lot of useful info there too.
- Securing Linux - Wall of text to some,wall of security goodness to others.
Commercial Tools
- AD Audit Plus - Real-time auditing of all things Active Directory
16-2 - Ensure that all accounts have an expiration date associated with the account.
This is more of a process, than a tool.
16-3 - Ensure that systems automatically create a report that includes a list of locked-out accounts, disabled accounts, accounts with passwords that exceed the maximum password age, and accounts with passwords that never expire.
Tools
- AD Info Free - Although the automation part is only available in the standard edition.
- Powershell - disabled accounts
- Powershell - password exceeds max age (and other commands)
- Powershell - passwords that never expire
16-4 - Establish and follow a process for revoking system access by disabling accounts immediately upon termination of an employee or contractor.
This is more of a process than a tool. Just remember to get all the accounts a user had access to, not just AD.
16-5 - Regularly monitor the use of all accounts, automatically logging off users after a standard period of inactivity.
Tools
Be careful setting these. Data loss may occur.
- Linux - Shell users
- Linux - Shell, X sessions, and TTYs
- Windows - A couple different methods outlined by native Spiceworks users.
- GPO - for Terminal Servers
- GPO - several methods depending on the situation
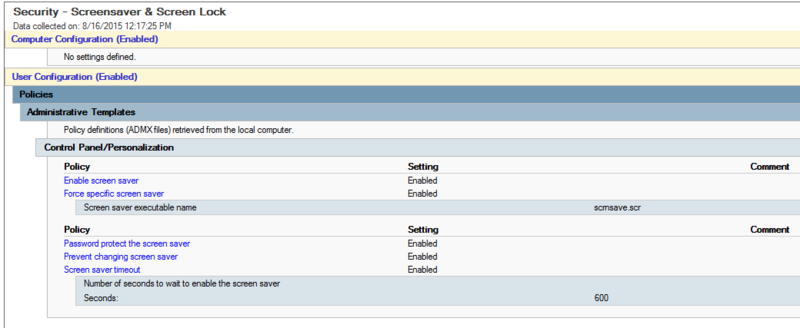
16-6 - Configure screen locks on systems to limit access to unattended workstations.
Tools
- GPO - Windows 2012 server and Windows 8+ clients.
- GPO - Auto lock after 10 minutes of activity:
16-7 - Monitor account usage to determine dormant accounts, notifying the user or user's manager. Disable such accounts if not needed, or document and monitor exceptions (e.g., vendor maintenance accounts needed for system recovery or continuity operations).
Free Tools
- Inactive User Tracking - by Netwrix, auto build and send reports via email
- Powershell - You will have to automate the report notifications
16-8 - Require that all non-administrator accounts have strong passwords that contain letters, numbers, and special characters, be changed at least every 90 days, have a minimum age of one day, and not be allowed to use the previous 15 passwords as a new password.
Free Tools
- Fine-Grained Password Policies - specify multiple password policies within a single domain. You can use fine-grained password policies to apply different restrictions for password and account lockout policies to different sets of users in a domain.
- TechNet - Best Practices for effective password policies
16-9 - Use and configure account lockouts such that after a set number of failed login attempts the account is locked for a standard period of time.
Free Tools
- GPO - configure account lockout policies
- Troubleshoot locked accounts - Troubleshoot where account lockouts are coming from
16-10 - Require that managers match active employees and contractors with each account belonging to their managed staff. Security or system administrators should then disable accounts that are not assigned to active employees or contractors.
This is more of a policy than a tool
16-11 - Monitor attempts to access deactivated accounts through audit logging.
You can configure your SIEM to do this. Covered in section 3-8
16-12 - Configure access for all accounts through a centralized point of authentication, for example, Active Directory or LDAP. Configure network and security devices for centralized authentication as well.
Free Tools
- 389 Directory - Open Source LDAP server based on Fedora Linux
- Apache DS - Directory server written in Java
- Oracle Internet Directory - Oracles implementation, based on LDAP v3
16-13 - Profile each user's typical account usage by determining normal time-of-day access and access duration. Reports should be generated that indicate users who have logged in during unusual hours or have exceeded their normal login duration.
Commercial Tools
- ADAudit Plus - Real-Time Monitoring of User Logon Actions with alerting and reporting
16-14 - Require multi-factor authentication for accounts that have access to sensitive data or systems.
This is covered in section 12-12
16-15 - For authenticated access to web services within an enterprise, ensure that account usernames and passwords are passed over an encrypted channel and associated password hash files are stored securely if a centralized service is not employed.
If you're not sure if your login form on website X is passing the login credentials in clear text, you can find out with Wireshark. SolarWinds also offers a free tool to use with Wireshark pcap files called Response Time Viewer for Wireshark.
16-16 - Configure all systems to use encrypted channels for the transmission of passwords over a network.
This is more of a procedure than a tool.
16-17 - Verify that all password files are encrypted or hashed and that these files cannot be accessed without root or administrator privileges. Audit all access to password files in the system.
AUTHOR'S NOTE - Remember to use 15+ characters for passwords on Windows.
AUTHOR'S NOTE - Be familiar with Kerberos Golden Ticket Forgery vulnerability (also this)!
Free Tool
- GPO - How to prevent Windows from storing a LAN manager hash of your password in Active Directory and local SAM databases