This article was written by an independent guest author.
The reason why ransomware is more rampant today is simple: it’s lucrative for hackers. As high-profile examples of ransomware continue to skyrocket concerning the amount of ransom paid, hackers will only continue to pursue it as a strategy.
How the incentives are changing for hackers
As the degree of sophistication with which attackers use to victimize businesses rises, so does the price of the average ransom. In a relatively short period, ransomware has transformed from a minor cybersecurity issue to a multi-billion-dollar industry.
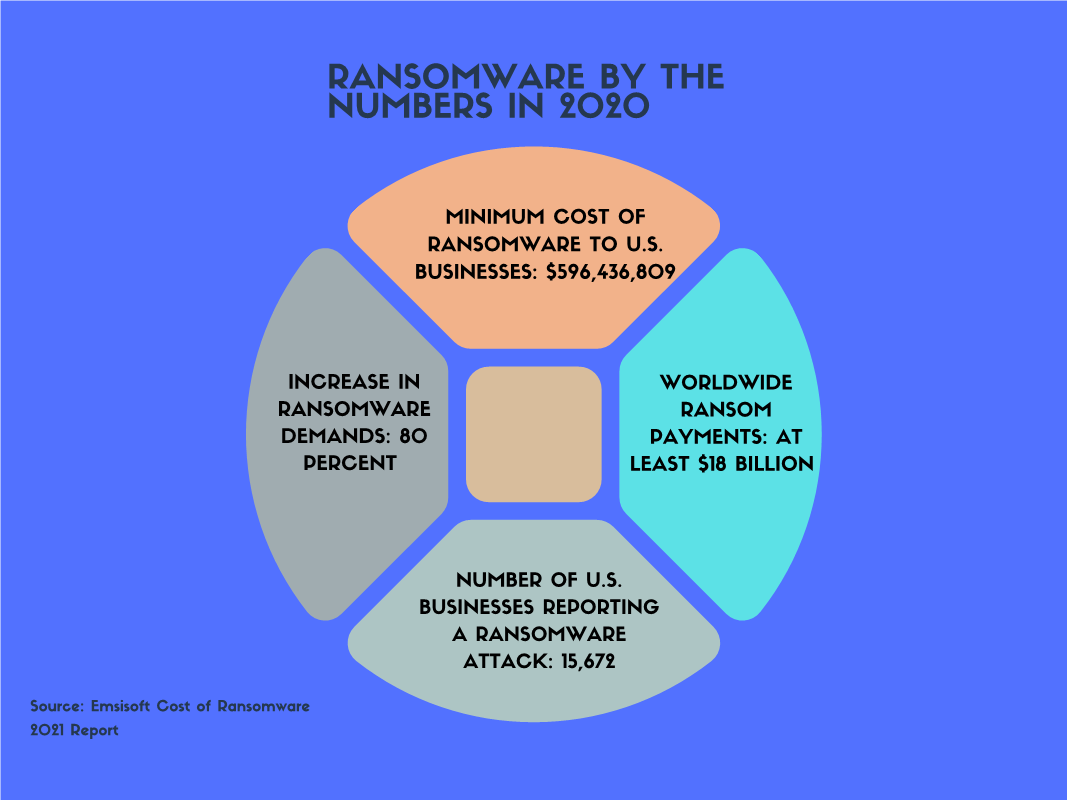
According to a 2021 Emsisoft report, 2020 was a profitable year for hackers: the average ransom demand ballooned by over 80 percent. Worldwide, at least $18 billion was paid in ransoms, which doesn’t factor in the costs associated with downtime for both public and private sectors. In the United States alone, almost 16,000 businesses were victimized by ransomware, bringing in nearly $600 million for hackers.
Proactive strategies to prevent ransomware incidents
One of the easiest methods an organization can use to protect itself from ransomware is adherence to strict backup processes. Ransomware is only getting more sophisticated, and many of your fail safes may not protect you from the latest hacker tactics. Like so many other facets of IT, it’s a case of “backups to the rescue”. However, in far too many ransomware attacks, the victims could not complete a full recovery for various reasons. In some cases, it was too much time from the last backup, and in others, backups were stored on the same network as the ransomware attack.
Taking the time to focus on your backup processes is well worth the investment. Because today, your backups should be considered as part of your organization’s “crown jewels.”
Aside from backups, the old cybersecurity mantra about the superiority of protection above detection holds true here. To truly mitigate these threats and reduce your attack surface, being proactive is critical.
Here are a few options to consider to proactively protect your attack surface:
-
Security awareness training
Your organization can have all the best technology at its disposal to prevent threats, but if your employees are not careful about the emails they open or the links they click, the technology won’t help you. Your employees are the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain — that includes everyone — from the C-suite to the boardroom to all stakeholders. Corporate cultures that place greater importance on cybersecurity typically put those organizations in a better position to prevent ransomware.
-
Zero trust architecture and micro segmentation
In many ransomware cases, hackers gain access to one segment of a network and then freely move laterally to other network segments to obtain the “crown jewels”. But what if the hackers are unable to move within your network and get stuck in one small, data-free segment? That’s the concept of micro segmentation, in which only certain users can access critical applications and networks. By default, access requests from additional users or applications are blocked.
A Zero trust architecture improves upon the micro segmentation strategy, by incorporating authentication and identity management, encryption, vulnerability and patch management, and comprehensive monitoring of devices, traffic and applications.
While Zero trust should be your ultimate goal, adopting the architecture requires significant planning. Deploying micro segmentation should be the bare minimum in efforts to reduce ransomware.
Endpoint protection
In the fight against ransomware, endpoint protection is a tool that prevents the ransomware program from even installing and running on the infected device. Taking endpoint protection a step further, endpoint protection and response (EDR) can detect the threat, analyze its nature, and alert your team about the How, What, and Where of the attack. EDR solutions essentially contain the threat and prevent it from spreading
How consultants can help
If your organization falls victim to ransomware, the damage extends well beyond the financial costs. With a ransomware attack, timing is everything. In the first quarter of 2021, a Coveware study reports that the average amount of downtime due to a ransomware attack was 23 days, up ten percent from the previous quarter.
Responding to a ransomware attack is an integral part of your incident management program. But in too many cases, resources for IT teams are stretched thin. Working with a managed incident response team, you get the experience and expertise of cyberdefense consultants to either lead the investigation or supplement your internal IT or cybersecurity team.
With AT&T Cybersecurity incident response service, you’ll be well-positioned to:
- Prevent data breaches
- Quickly respond to attacks and mitigate impact
- Minimize impacts of a potential breach
- Quickly analyze and recover from the breach
- Mitigate security risk
- Improve incident response
- Leverage an “all hands on deck” approach, which includes in-depth digital forensic analysis, breach, support and compromise detection
It is also important to conduct periodic vulnerability assessments to find and patch potential security weaknesses. While there are many options on the market, your organization can take advantage of the unlimited 30 day trial offer from AT&T.
At the end of the day, the very best way to protect against ransomware is to work with experts to protect against the attacks. Because even the best and most security-aware employees may one day fall for a sophisticated phishing email that leads to ransomware. If an attack occurs, knowing you can rely on experts to conduct the forensic investigation to mitigate the risk can make all the difference.