Traditional cyber security strategy focuses on blocking known cyber threats and attack vectors. This strategy revolves around vulnerability assessment, active defense using the IDS and firewall, and an incident response plan to handle critical situations after a security breach. The overall strategy depends on pre-identified threats and tools designed to find and block known malware and attack vectors. But, what if attackers use new techniques or tools? The well-known and carefully drafted cyber security strategy can’t help defend you in that case, and at the end of the day the CISO may get fired.
The Only Thing That Is Constant Is Change -” – Heraclitus
The ever-changing cyber security world has to offer more than before. You should not expect attackers to use the same techniques every time - you need to take a proactive approach to discover what is happening to others and learn from their mistakes.
Incorporating cyber threat intelligence with your cyber security strategy helps you to fight against cybercrime. Regular monitoring and reporting of emerging threats and vulnerabilities can alert you to take timely action before an actual attack occurs. By using threat analysis, you can:
- Take proactive defense measures
- Narrow down focus areas and put the maximum effort where required
- Make procurement decisions (what software and hardware to buy in the future)
- Recruit people for your team with relevant skill sets
- Reduce false positives
- Convince or communicate with management about real dangers to the business
- Provide up-to-date information to the incident response team for their investigation
Traditional approach VS Intelligent approach
Cyber threat intelligence primarily focuses on external threats. Through collecting and processing threat information and generating the actionable information, it enhances cyber defense and helps stop attacks as quickly as possible.
Collecting Threat Intelligence
Organizations can access huge databases of malware signatures, logs and other threat vectors, but converting this information into intelligence is the real art. Let’s look into the threat indicators that really matter. The most common threat indicators are:
- Hashes (signatures)
- Compromised or malicious domains and IP addresses
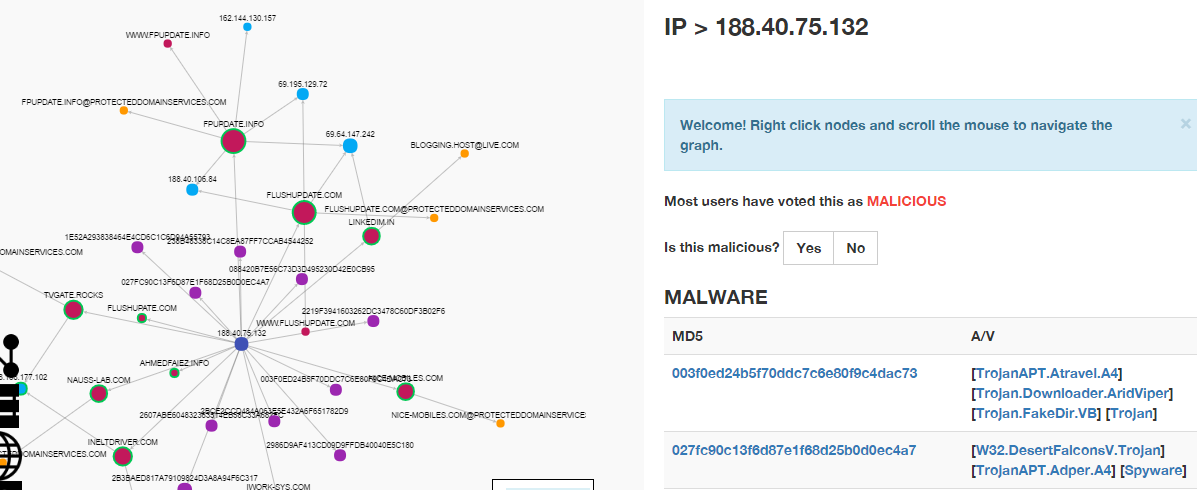
Malware spreading by phishing emails can be identified using its hash identifier. Hash is a unique identifier that every computer program has, and by collecting the updated information of the malware/virus hash file, you can alert your security solution to block the malicious file at its first entry. Apart from the malicious file, you should block the compromised domain hosting/spreading phishing pages, as well as track the blacklisted IPs and domains, and block their access so that they never reach your organization’s technology infrastructure. The risks associated with the threat indicators we've discussed are:
- Malware, spyware and backdoors
- Phishing, spam and other fraudulent activity
- Darknet IP addresses
- C&C (command and control) servers that manage botnets and instigate DDoS attack
- Anonymous proxies and P2P sharing websites
We utilize public and private data feeds to collect information about these threat indicators. Threatcrowd, also available in MALTEGO, is a well-known project providing feeds of blacklisted / malware-spreading websites with hash details.
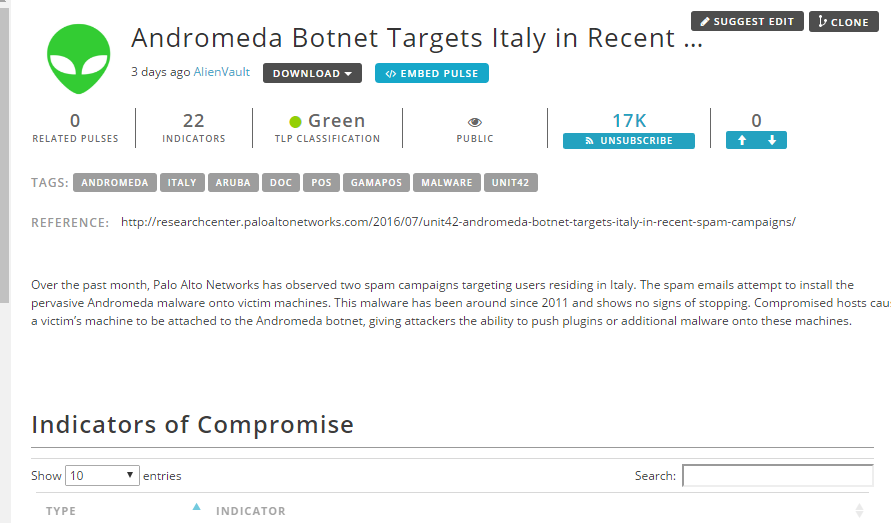
OTX (Open Threat Exchange) by AlienVault is an open threat intelligence sharing platform; it enables the community to share the actionable intelligence with other people. The pulses OTX provides contain detailed information about a threat with its IOC (indicators of compromise):
- Hostname and sub-domain
- Hashes (MD5, SHA1, SHA256 and others)
- IP addresses, domain and URLs
- File path and email addresses
It also provides brief information about the target, affected devices, method of propagation, and geo location (if applicable).
There are other services to mention:
- Malwr.com
- Virustotal.com
- Openphish.com
Threat Analysis
The most important step is to carefully analyze collected threats. Some threats may be:
- Invalid, unevaluated, or not important for you
- Lacking context or unable to target the network you are managing
- Not associated with any specific type of organization or enterprise
These types of alerts can distract security analysts. While analyzing threats, you need to clear the noise first. The solution is to validate and prioritize threats, assigning ranks to threats based on risk and then prioritizing based on the danger and level of vulnerability.
Incorporating threat intelligence with careful analysis can enhance your cyber security strategy and can help you to stay secure. Incident response can solve the issue, but it can’t completely resolve the situation, as lost confidential data can be retrieved or changed, and your brand’s reputation may be impacted. It takes time to gain trust - so you need to retain it by using threat intelligence and an intelligent cyber defense strategy.
About the Author:
Irfan Shakeel can be found @irfaanshakeel and LinkedIn.