This blog was jointly written with Ofer Caspi. Some of the links in this blog require an OTX account, and the QakBot infrastructure tracker will require readers to be customers with access to the Threat Intel subscription.. Thanks to the following researchers and the MalwareBazaar Project:
Executive summary
AT&T Alien Labs closely monitors the evolution of crimeware such as the QakBot (also known as Qbot) malware family and campaigns in connection with QakBot. The jointly coordinated takedown of the actors behind Emotet in late January has left a gap in the cybercrime landscape, which QakBot seems poised to fill.
Key Points:
- TA551 has added QakBot to its arsenal, which also includes IcedID.
- QakBot employs anti-virus evasion, anti-detection, and anti-sandbox tactics across the entire spectrum of the attack.
- The actor(s) behind QakBot possess a modular framework consisting of maldoc builders, signed loaders, and DLLs that produce initially low detection rates at the beginning of the attack, which creates opportunities to deliver additional malware such as Egregor and Cobalt Strike.
- The actor(s) responsible for QakBot have an active affiliate program.
- TA551, Cobalt Strike, and QakBot have all been observed jointly within the context of individual campaigns.
Analysis
Qakbot, also known as QBot or Pinkslipbot, is a modular information stealer. It has been active since 2007 and primarily used by financially motivated actors. It was initially known as a banking Trojan and a loader using C2 servers for payload delivery; however, its use expanded beyond strictly being a banking trojan. The hallmarks of a QakBot infection chain consist of a phishing lure (T1566) delivered via email chain hijacking or spoofed emails that contain context-aware information such as shipping, work orders, urgent requests, invoices, claims, etc. The phishing emails alternate between file attachments (T1566.001) and links (T1566.002). QakBot is often used as a gateway entry, similar to TrickBot or Emotet, that leads to post exploitation operations leveraging frameworks such as Cobalt Strike as well as delivering Ransomware.
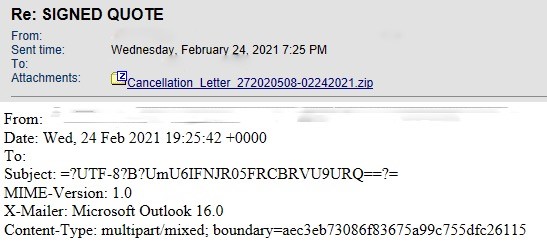
QakBot email lures are not the most sophisticated; however, by using contextually aware themes that originate from hijacked email chains or potentially compromised accounts within a user’s social circle, they are effective. Figure 1 below illustrates an example of a recent QakBot lure with the subject “Re: SIGNED QUOTE” and a ZIP file attachment labeled “Cancellation_Letter_272020508-02242021.zip”.
Figure 1. QakBot "Signed Quote" Email Lure
The actors further establish the trust and confidence of the targeted user by presenting a semi-official looking DocuSign graphic that guides the user through the process of enabling the Excel 4 Macros. A representative sample, 78ea3550e2697cd06b07df568242f7fc9f57e4d2b297b74f6ce26e97613de53a, seen in a recent QakBot campaign is shown in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2. QakBot DocuSign Lure
QakBot Excel spreadsheets often contain hidden spreadsheets, Excel 4.0 macros, spreadsheet formulas, and BIFF records all designed to pass a visual inspection from the user with the added benefit of bypassing detection mechanisms that attempt to parse multiple legacy formats inside the spreadsheet. Figure 3 below shows a screenshot of output from the open-source XLMMacroDeobfuscator tool, which decodes obfuscated Excel 4.0 macros.
Figure 3. XLMMacroDeobfuscator Output for a QakBot Excel 4.0 Macro Spreadsheet
Once the Excel 4.0 macro is decoded it is possible to see the CALL to URLDownloadToFileA, which downloads the QakBot DLL in this campaign from http[:]//rlyrt26rnxw02vqijgs[.]com/fera/frid[.]gif. Next, the EXEC function is evaluated which executes “rundll32.exe nxckew.wle, DllRegisterServer”. It is also a common tactic for QakBot to execute “regsvr32.exe -s nxckew.wle,DllRegisterServer”. Both instances are designed to evade sandbox environments that do not supply the expected command line arguments. A representative QakBot DLL analyzed by Alien Labs, 9a353d4b85b3097762282703f1807c2b459698966b967280c8e4e13cc56d2e28, has two exports: the entry point (0x10005a5d) and DllRegisterServer (0x10029c88)and if DllRegisterServer is not called via regsvr32.exe or rundll32.exe with command line options, then only the entry point is called and the malicious code in DllRegisterServer is not called. Figure 3 below shows improved readability and de-obfuscation of the macro by manually replacing and substituting the cell values and formulas.
Figure 3. Better de-obfuscation of the spreadsheet
The results of our additional de-obfuscation efforts are confirmed when the QakBot Excel spreadsheet is run inside a sandbox in Figure 4 below.
Figure 4. OTX screenshot showing the “rundll32 ..\nxckew.wle, DllRegisterServer'' execution
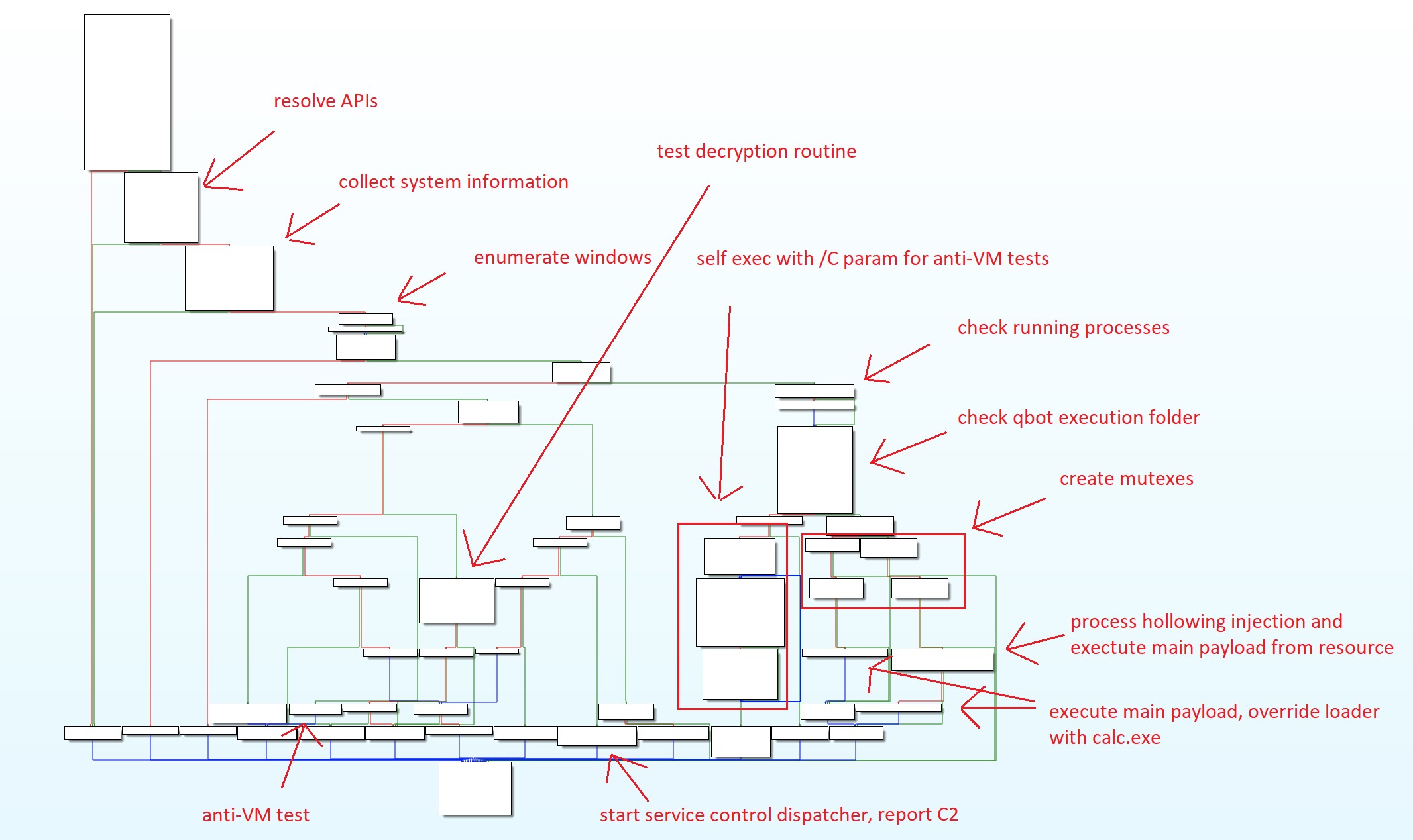
Before executing the main payload, the QakBot loader will first test the infected system to see if it is a good candidate for infection. The QakBot loader is responsible for checking its environment to include whether it is running on a Virtual Machine, identifying any installed and running security and monitoring tools such as AntiVirus products or common security researcher tools. Figure 5 below shows a high-level execution flow of the QakBot loader.
Figure 5. QakBot Execution Flow
To make detection and analysis harder, QakBot encrypts its strings and decrypts them at runtime before use. Once the QakBot execution logic is finished using a string, it will immediately delete the string from memory. An example of this can be seen in Figure 6 below, which shows QakBot decrypting a string containing the value for lpProcName passed as a parameter to the GetProcAddress API call. The selected function, which has been labeled in IDA Pro as, “oc_clear_mem” deletes the string memory right after it retrieves the process address.
Figure 6. QakBot GetProcAddress and clear_mem routines
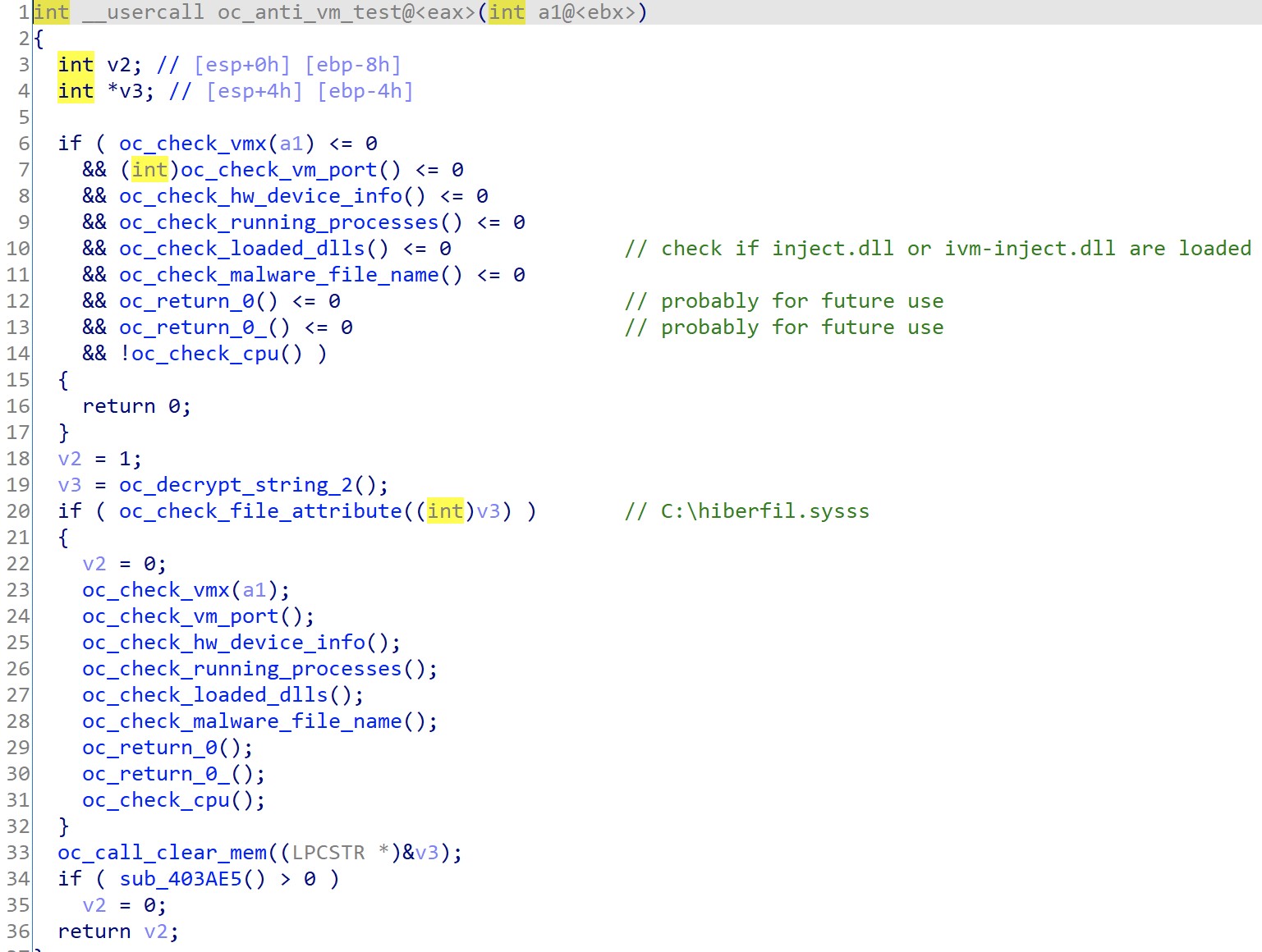
When executed, QakBot will check whether it has previously been executed on the machine by checking for the specified malware folder. If QakBot discovers it is a first time run, it will relaunch itself from cmd.exe with the /C parameter that will inform the loader to proceed and run its Anti-VM checks on the machine and return the results to the parent process. If QakBot detects it is running in a VM environment, then the final payload will not be decrypted since QakBot uses the return value from these checks in its final decryption routine. Figure 7 below shows the QakBot environment check logic.
Figure 7. QakBot Environment Check Logic
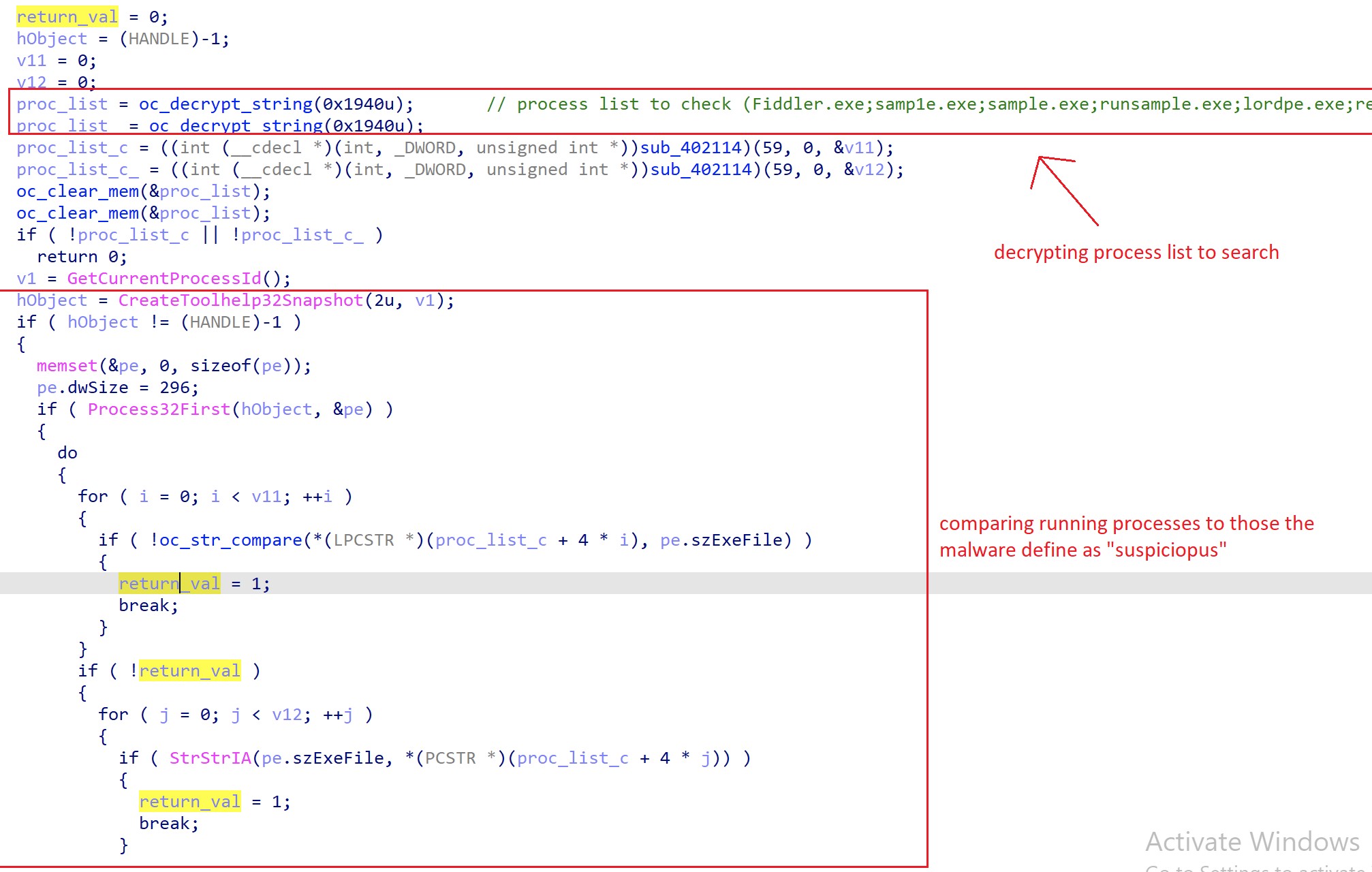
Specifically, QakBot checks the system for the names of running processes that match the strings listed in Table 1 below.
|
PROCESS NAMES |
||
Autoruns.exe |
bds-vision-agent-app.exe |
bds-vision-agent-nai.exe |
bds-vision-apis.exe |
CFF Explorer.exe |
dsniff.exe |
dumpcap.exe |
Fiddler.exe |
HashMyFiles.exe |
idaq.exe |
idaq64.exe |
lordpe.exe |
MultiAnalysis_v1.0.294.exe |
netmon.exe |
OLLYDBG.EXE |
pr0c3xp.exe |
ProcessHacker.exe |
Procmon.exe |
Procmon64.exe |
regshot.exe |
ResourceHacker.exe |
runsample.exe |
samp1e.exe |
sample.exe |
Tcpview.exe |
TPAutoConnect.exe |
VBoxService.exe |
VBoxTray.exe |
VGAuthService.exe |
vm3dservice.exe |
vmacthlp.exe |
vmtoolsd.exe |
windbg.exe |
Wireshark.exe |
x32dbg.exe |
x64dbg.exe |
Table 1. AntiVM process name checks for security, monitoring, and analysis tools
Figure 8 below shows the decryption routine for the security and monitoring tool strings (T1140).
Figure 8. QakBot decrypting tool check strings
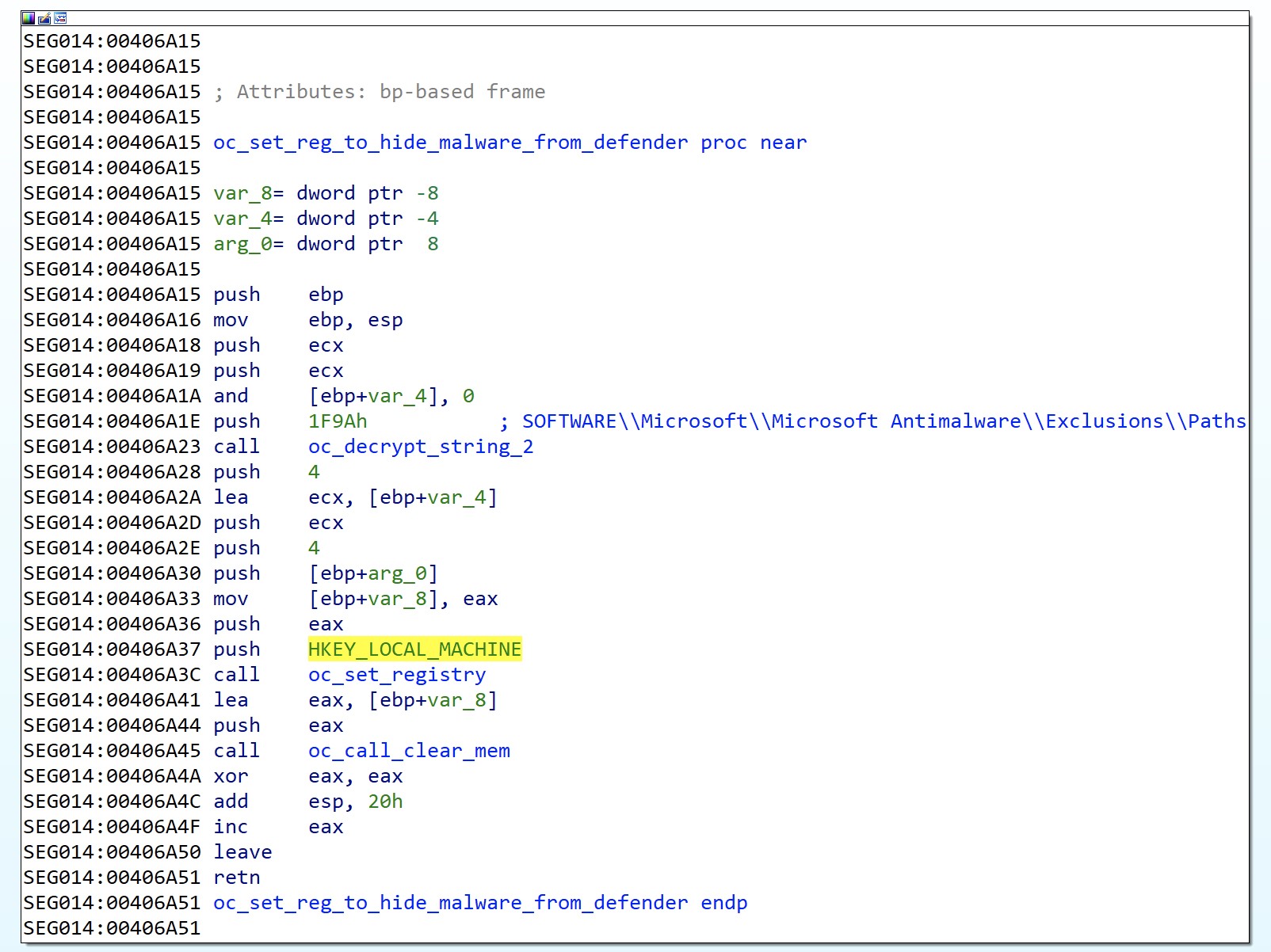
QakBot will also add its folder to the Windows Defender exclusions setting located in the Registry (T1112), which prevents Defender from scanning QakBot artifacts. The Registry location can be seen in Figure 9 below.
Figure 9. QakBot adding exclusion paths to Windows Defender settings
In addition to the previously mentioned environment check, QakBot collects system information (T1082) such as computer name, system directories, user profiles, and more, which is shown in Figure 10 below.
Figure 10. QakBot system information collection
QakBot will use process hollowing (T1055.012) in order to inject itself into explorer.exe. If it is unsuccessful then QakBot will attempt to inject itself into mobsync.exe or iexplore.exe. The screen shot in Figure 11 illustrates the QakBot process name decryption routine.
Figure 11. QakBot routine to decrypt process names for injection
Figure 12 below shows the QakBot logic to overwrite the suspended explorer.exe process and then resume its execution.
Figure 12. QakBot process hollowing routine
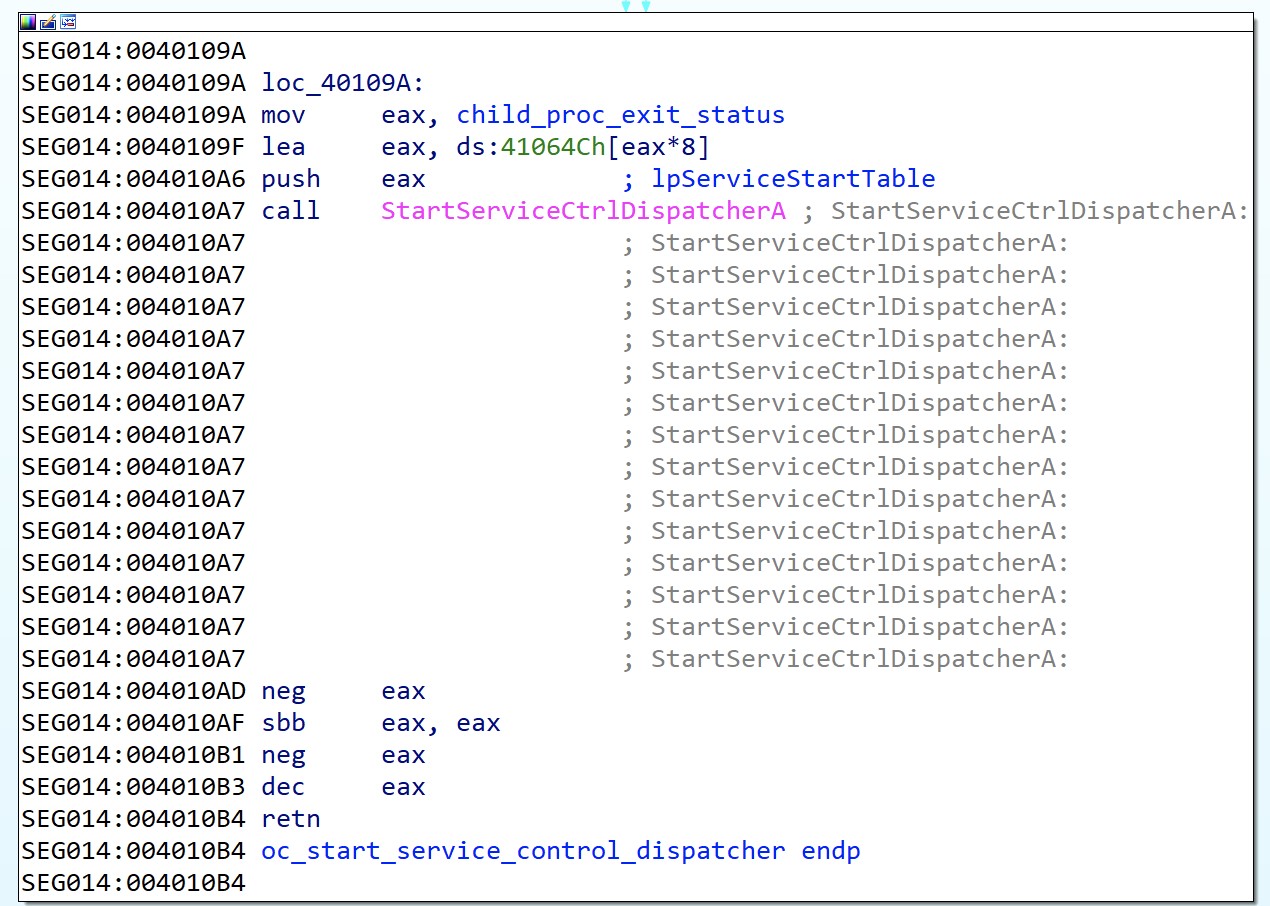
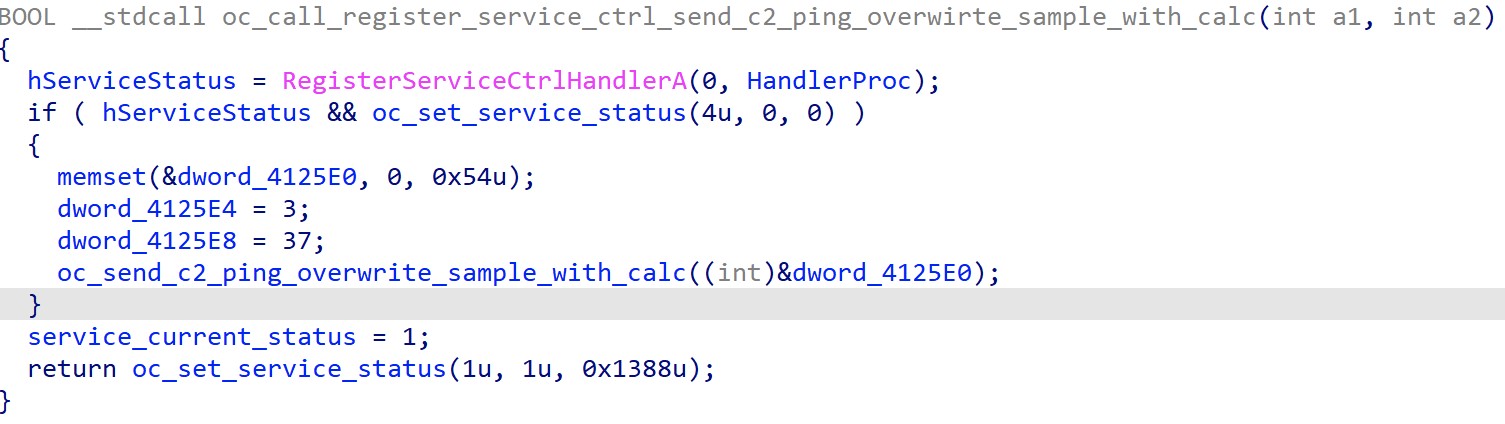
Additionally, QakBot abuses the Service Control Manager (SCM) to create a child process, which is then detached from the parent when the SCM terminates the parent process. QakBot C2 communications begin in this stage to make it more difficult to monitor. Figure 13 below shows the SCM spawned process abuse technique.
Figure 13. QakBot abusing SCM to spawn a detached process
Figure 14 below shows the QakBot C2 ping during the SCM interaction.
Figure 14. QakBot sending C2 ping
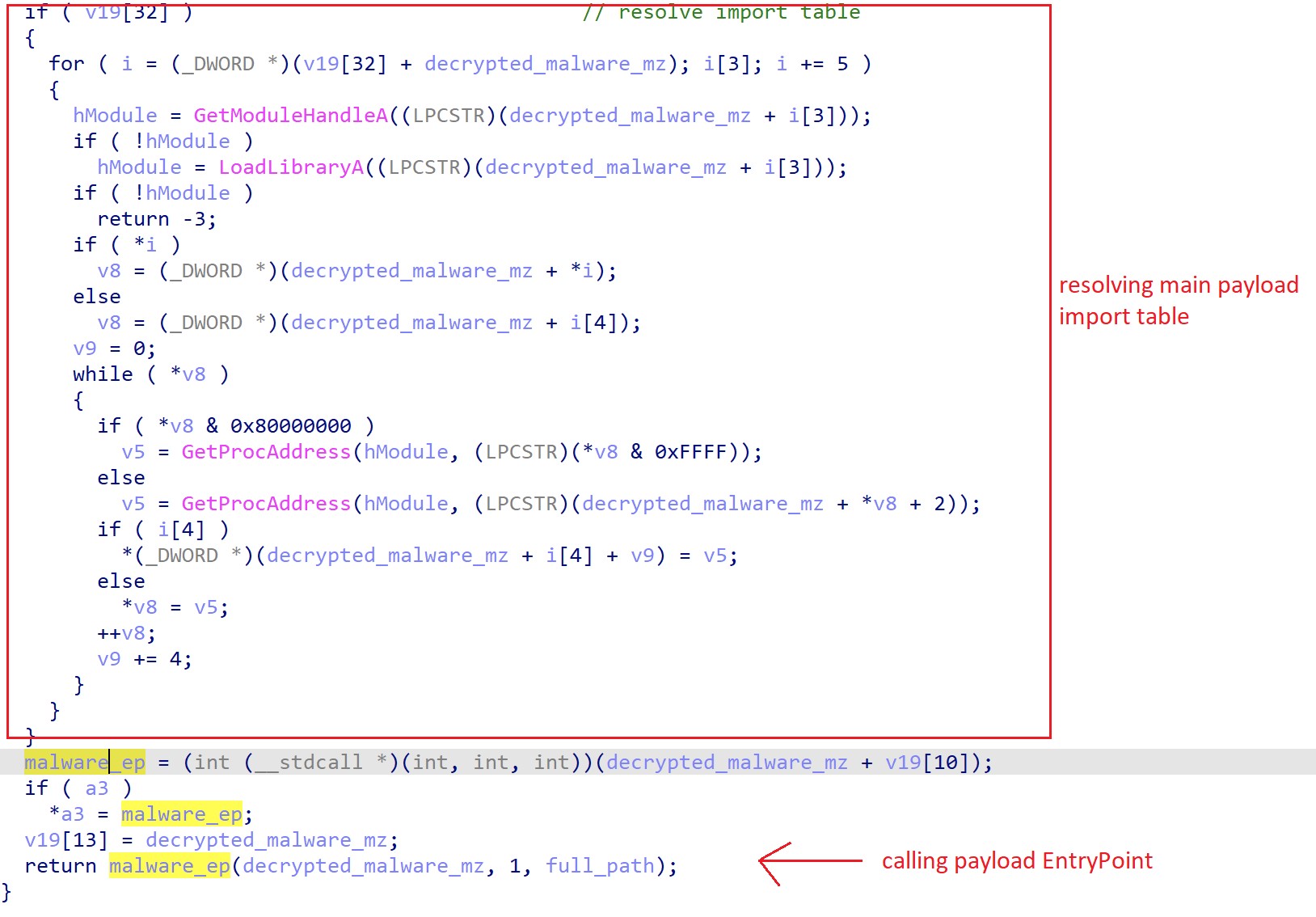
Finally, if the QakBot loader has verified its execution environment has passed its tests, then QakBot will proceed to decrypt and execute the main QakBot payload, which is hidden as resource “307”. The decryption and import table resolution of its main payload is shown in Figure 15 below.
Figure 15. QakBot decryption and import table resolution of main payload
The combined anti-analysis and evasion techniques across the infection chain significantly impair antivirus, EDR, and other security defenses from detecting and preventing the initial infection. Despite the limitations and challenges presented by QakBot DLLs there is ample opportunity to detect QakBot loaders signed by revoked and blacklisted malicious certificates. Alien Labs has identified 42 unique signers and signature serial numbers, which are included in Detection Methods section to aid in detection and hunting with YARA and Osquery. Additionally, there are a number of behavioral patterns, Indicators of Behavior (IOB), which provide opportunities for detection.
Recommended actions
- Search for a renamed version of “wmic.exe” such as “xml.com”, which spawns “regsvr32.exe” and executes files with JPG or GIF file extensions.
- Regularly perform process auditing and accounting looking for process oddities such as
- parent to child relationships “excel.exe” spawning “rundll32.exe”.
- Instances of “WerFault.exe” executing without a command line.
- “esentutl.exe” executing with a command line containing the term “WebCache”.
- Check for unrecognized exclusions, files or folders, in Windows Defender settings.
Conclusion
Alien Labs has observed QakBot over the past three months being used in a role similar to TrickBot, which includes malspam delivery, stealthy maldocs dropping signed loaders, establishing a foothold, and finally post exploitation activities such as lateral movement, access operations, and ransomware delivery. Alien Labs actively tracks the QakBot C2 infrastructure for customers, which is available via OTX here.
Detection methods
The following associated detection methods are in use by Alien Labs. They can be used by defenders to tune or deploy detections in their own environments or for aiding additional research.
|
AGENT SIGNATURES |
| SELECT process.pid as source_process_id, process.name as source_process, process.path as file_path, authenticode.result, authenticode.serial_number as certificate_serial_number, authenticode.issuer_name as certificate_issuer_name, authenticode.subject_name as certificate_subject_name, parent_processes.path as source_process_parent, parent_processes.cmdline as source_process_parent_commandline, parent_processes.uid as parent_uid, hashes.sha256 AS file_hash_sha256 FROM processes as process LEFT JOIN authenticode ON process.path = authenticode.path LEFT OUTER JOIN processes parent_processes ON process.parent = parent_processes.pid LEFT JOIN hash AS hashes ON hashes.path = process.path WHERE authenticode.serial_number IN ('00ac307e5257bb814b818d3633b630326f', '186d49fac34ce99775b8e7ffbf50679d', '02b6656292310b84022db5541bc48faf', '17d99cc2f5b29522d422332e681f3e18', '142aac4217e22b525c8587589773ba9b', '00ca646b4275406df639cf603756f63d77', '0cf2d0b5bfdd68cf777a0c12f806a569', '7ab21306b11ff280a93fc445876988ab', '00f097e59809ae2e771b7b9ae5fc3408d7', '00d3356318924c8c42959bf1d1574e6482', '00e38259cf24cc702ce441b683ad578911', '00b61b8e71514059adc604da05c283e514', '51cd5393514f7ace2b407c3dbfb09d8d', '00b2e730b0526f36faf7d093d48d6d9997', '3cee26c125b8c188f316c3fa78d9c2f1', '7156ec47ef01ab8359ef4304e5af1a05', '5c7e78f53c31d6aa5b45de14b47eb5c4', '00dadf44e4046372313ee97b8e394c4079', '00f8c2e08438bb0e9adc955e4b493e5821', '70e1ebd170db8102d8c28e58392e5632', '00c167f04b338b1e8747b92c2197403c43', '00e04a344b397f752a45b128a594a3d6b5', '00a7989f8be0c82d35a19e7b3dd4be30e5', '08622b9dd9d78e67678ecc21e026522e', '3696883055975d571199c6b5d48f3cd5', '5b440a47e8ce3dd202271e5c7a666c78', '690910dc89d7857c3500fb74bed2b08d', '00d59a05955a4a421500f9561ce983aac4', '00c2fc83d458e653837fcfc132c9b03062', '016836311fc39fbb8e6f308bb03cc2b3', '4743e140c05b33f0449023946bd05acb', 'aa28c9bd16d9d304f18af223b27bfa1e', '00d627f1000d12485995514bfbdefc55d9', '6e0ccbdfb4777e10ea6221b90dc350c2', '1249aa2ada4967969b71ce63bf187c38', '00e5ad42c509a7c24605530d35832c091e', '38989ec61ecdb7391ff5647f7d58ad18', '1a311630876f694fe1b75d972a953bca', '4a7f07c5d4ad2e23f9e8e03f0e229dd4', '00d4ef1ab6ab5d3cb35e4efb7984def7a2', '37f3384b16d4eef0a9b3344b50f1d8a3', '4e7545c9fc5938f5198ab9f1749ca31c'); |
Associated indicators (IOCs)
The following technical indicators are associated with the reported intelligence. A list of indicators is also available in the OTX Pulse. Please note, the pulse may include other activities related but out of the scope of the report.
|
TYPE |
INDICATOR |
DESCRIPTION |
|
HOSTNAME |
1[.]nvprivateoffice[.]info |
QakBot C2 |
|
SHA256 |
17cd3c11fba639c1fe987a79a1b998afe741636ac607254cc134eea02c63f658 |
QakBot Maldoc Lure |
|
SHA256 |
3be905066595dc785c9b6b98bfb2d9e0478f32df31337a8aeec96d7ccd52769e |
QakBot Loader |
|
SHA256 |
6850bd6206735cc62b932900fceddfd7218e30a9f4b82c84cb15a0060726b436 |
QakBot DLL Final Payload |
|
SHA256 |
bf9efaf79a6990bbd9b378d05a609e0ad9d3a501a56a85e04479682435c22b0a |
Signed QakBot Loader, Signer “SHOECORP LIMITED” |
|
SHA256 |
03412f800b9b512258e462aed00ee5725fcb970979e828d43069877e06a38f28 |
Signed QakBot Loader, Signer “DILA d.o.o.” |
|
SHA256 |
43d20a15d5e9cd51454a35946d762687cc2921a4581844ae32acd86427aadaab |
Signed QakBot Loader, Signer “PKV Trading ApS” |
|
SHA256 |
0f597a709ad87855695a88a71c46b690d1049d01da1d30c47927d8acba5fcc23 |
Signed QakBot Loader, Signer “A.B. gostinstvo trgovina posredništvo in druge storitve, d.o.o.” |
Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK
The findings of this report are mapped to the following MITRE ATT&CK Matrix techniques:
- Initial Access
- T1566: Phishing
- T1566.001: Spearphishing Attachment
- T1566.002: Spearphishing Link
- T1566.003: Spearphishing via Service
- T1566: Phishing
- Execution
- T1204: User Execution
- T1204.001: Malicious Link
- T1204.002: Malicious File
- T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter
- T1059.005: Visual Basic
- T1053: Scheduled Task/Job
- T1053.005: Scheduled Task
- T1129: Shared Modules
- T1106: Native API
- T1047: Windows Management Instrumentation
- T1204: User Execution
- Defense Evasion
- T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information
- T1027.002: Software Packing
- T1553: Subvert Trust Controls
- T1553.002: Code Signing
- T1218: Signed Binary Proxy Execution
- T1218.010: Regsvr32
- T1497: Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion
- T1497.001: System Checks
- T1497.002: User Activity Based Checks
- T1497.003: Time Based Evasion
- T1112: Modify Registry
- T1070: Indicator Removal on Host
- T1070.004: File Deletion
- T1140: De-obfuscate/Decode Files or Information
- T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information
- Command and Control
- T1090: Proxy
- T1090.003: Multi-hop Proxy
- T1105: Ingress Tool Transfer
- T1090: Proxy
- Privilege Escalation
- T1055: Process Injection
- T1055.012: Process Hollowing
- T1055: Process Injection
- Discovery
- T1082: System Information Discovery
- T1049: System Network Connections Discovery
- T1016: System Network Configuration Discovery
- T1057: Process Discovery
- T1033: System Owner/User Discovery
- T1518: Software Discovery
- T1518.001: Security Software Discovery
- Persistence
- T1546: Event Triggered Execution
- T1547: Boot or Logon Autostart Execution
- T1547.001: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder