Executive summary
Crypto miners are determined in their objective of mining in other people's resources. Proof of this is one of the latest samples identified with LevelBlue Labs, with at least 100 different loaders and at least 4 different stages to ensure their miner and backdoor run smoothly in the infected systems.
Key takeaways:
- Attackers have been sending malicious attachments, with a special emphasis on Mexican institutions and citizens.
- The techniques observed in these samples are known but still effective to keep infecting victims with their miners. Reviewing them assists in reminding defenders the current trends and how to improve their defenses.
- The wide variety of loaders in conjunction with the staged delivery of the miner and backdoor malwares, shows how determined the attackers are to successfully deliver their payloads.
Analysis
Crypto miners have been present in the threat landscape for some years, since an attacker identified the opportunity of leveraging victim’s CPUs to mine cryptocurrencies for them. Despite the current rough patch in the world of cryptocurrencies, these miners are still present and will be in the foreseeable future.
As seen in the current analysis, unlike IoT malwares, which also attempt to reach the biggest number of infected devices as possible, these miners target victims through phishing samples. The techniques used by these malwares are usually focused on reaching execution, avoiding detection to run under the radar and gaining persistence to survive any reboot.
A new miner sample showed up in April on LevelBlue Labs radar, with a wide range of different loaders aiming to execute it in infected systems up to this day. The loaders were initially delivered to the victims through an executable disguised like a spreadsheet. For example, one of the samples (fd5131645025e199caa142c12cef34b344437a0f58306f9b66c35d32618665ba) carries a Microsoft Excel icon, but its file extension corresponds to an executable.
A wide range of decoy documents were found associated with this miner, many of them associated with Mexican civilians: exam results, dentist results, Mexican Governmental documents, Mexican Social Security, Tax returns, etc. Figure 1 corresponds to one of the spreadsheets observed. The campaign identified in this report materialized most of its attacks during the second half of June 2022. For example, the mentioned file above was compiled in late May 2022 and was first observed in the wild a month after, on June 20, 2022.
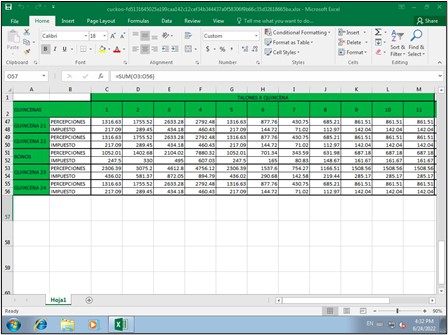
Figure 1. Decoy spreadsheet ‘ppercepciones anuales.xlsx’.
At the time of execution, the first activities performed are registry changes to cloak the malware samples. For example, by setting ‘HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\HideFileExt’ to 1, the attackers are hiding the file extensions and camouflaging the executables as documents. Additionally, the registry key ‘HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Hidden’ is set to 0 to avoid displaying in explorer the hidden files dropped during execution. Finally ‘ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin’ is set to 0 in order to execute any future samples with elevated privileges without explicit consent in the form of a pop up or inserting credentials.
The initial payload drops another executable file while opening the spreadsheet in Figure 1. This additional executable attempts to look like a legitimate executable. It is named ‘CmRccService.exe’ and has the same filename as the metadata associated with the product’s name, description and comments. It is probably an attempt to masquerade the process by making it similar to the legitimate Microsoft process ‘CmRcService.exe’ (Configuration Manager Remote Control Service) (T1036.004). However, the legitimate files owned by Microsoft would have been signed with Microsoft certificate, which is not the case for these files - which have not been signed at all.
Pivoting by this indicator, returns over a hundred different samples that have been created and delivered during the last three months, most of them in the last weeks. In addition to the product name ‘CmRccService.exe’, a similar decoy name was observed in this campaign ‘RegistryManager.exe’, which showed up in at least 6 different samples. The RegistryManager samples even carry a Copyright flag associated with Microsoft Corporation, lacking once again the corresponding file signature. These files are allocated under the folder ‘C:\Windows\ImmersiveControlPanel’ in an attempt to make the processes look as legitimate as possible.
Persistence of the whole process is attempted during the execution of ‘CmRccService.exe’. A new service is registered in the system (T1543.003), to be run with highest privileges each time the user logs on.
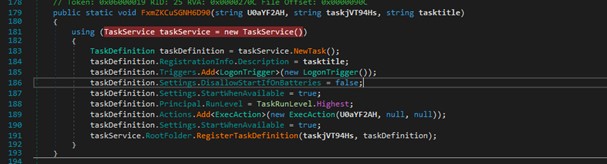
Figure 2. Persistence mechanism.
This loader reaches out to several domains hosting the payloads for next stages, configuration files and one-line commands to be executed.
One of these domains is ‘bekopgznpqe[.]is’. Initially created on February 22, 2022 with the name server 1984 Hosting Company, who offers domain names registration free of charge. However, since this behavior indicator makes the domain look suspicious to security companies, the domain was moved to Cloudflare on April 21 (a different nameserver with a better reputation due to its popularity and absence of free offerings). This technique has historically been used to improve the reputation of domains right before they are used during a campaign.
Additionally, the malware attempts to contact a supplemental domain ’dpwdpqshxux[.]ru,’ which does not yet resolve but was created on February 21, 2022, a day before ‘bekopgznpqe’ domain. There is no historical data of it ever resolving to any IP. For this reason, the domain is probably a backup plan, to be used if the first stops working.
The third and last domain identified during analysis did not follow the above pattern. The domain ‘2vkbjbpvqmoh[.]sh‘ was created in January 2022 in the Njalla name server, known and marketed as a great offering for ‘Privacy as a Service’ for domains and VPNs. After some time operating, the domain was marked for deletion in May 2022.
Before executing the third stage payload, Cmrcservice performs several modifications to the FireWall to allow inbound and outbound connections to the files it will drop afterwards. The executed command for these changes is ‘'C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe' /C powershell New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'RegistryManager' -Direction Inbound -Program 'C:\Windows\ImmersiveControlPanel\RegistryManager.exe' -Action Allow’.
Furthermore, the malware includes exclusions to the Microsoft Windows Defender for the folders from where the malware will be executing or the files it intends to execute (T1562). The command used for this purpose is ‘powershell.exe $path = 'C:\Windows\Branding\oidz.exe' ; Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath $path -Force’. The excluded folders and files include:
- C:\Users
- C:\Windows
- C:\Windows\Temp
- C:\Windows\ImmersiveControlPanel
- C:\Windows\ImmersiveControlPanel\CmRccService.exe
- C:\Windows\Branding
- C:\Windows\Branding\umxn.exe
- C:\Windows\Branding\oidz.exe
- C:\Windows\Help\Windows
- C:\Windows\Help\Windows\MsMpEng.exe
- C:\Windows\IME
The third stage payload is formed by the ‘p.exe’ executable, which doesn’t hide its contents, since the file’s metadata claims the filename is ‘payload.exe’. During execution, p drops two additional files: ‘oidz.exe‘ and ‘umxn.exe’, which correspond to the final payloads. Figure 3 recaps the execution flow until this point.
Figure 3. Execution tree.
‘Oidz.exe‘ runs an infinite loop, as seen in Figure 4, that will reach out to the Command & Control (C&C) looking for new commands to execute. After execution, it includes a sleep command to separate the requests for additional commands as well as its executions. In other words, this executable corresponds to the backdoor installed in the system.
The commands to be executed are uploaded by the attackers to the C&C servers, and oidz reaches out to specific files in the server and executes them, allowing the attackers to maintain any payload updated or modify its capabilities (T1102.003). This file does not aim to be persistent in the system since the grandparent process ‘Cmrcservice.exe’ already is. The C&C servers list seen in Figure 5, has a first parameter corresponding to the command to execute, while the second parameter corresponds to the flag of the command to be executed. This list of domains corresponds to the one used previously by ‘CmRccService’.
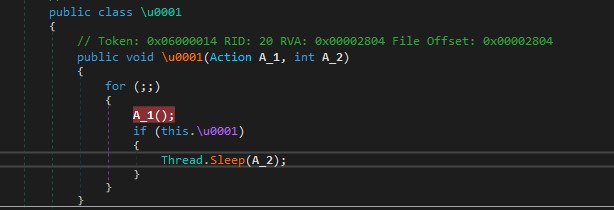
Figure 4. Oidz infinite loop.
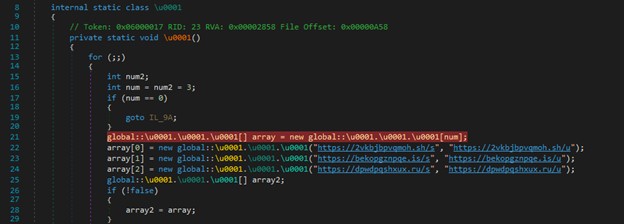
Figure 5. C&C list.
Finally, ‘umxn.exe’ corresponds to the crypto miner that will run with the configuration pulled from one of the C&C and stored in ‘%windir%\Help\Windows\config.json’. All the other files were preparing the environment for the miner, avoiding issues with execution, network communications or enabling modifications during the execution with the backdoor.
Since it was first observed in April 2022, some of the executables have changed names or had some variations but have been excluded throughout the report to avoid confusion. The execution line in this report and observed in Figure 3 is the most common one observed. One of the most remarkable mentioned variations, include file ‘MsMpEng.exe’ or ‘McMpEng.exe’, which is an additional stage executed by ‘umxn.exe’. This sample claims in its PE metadata to be ‘Antimalware Service Executable’ to disguise its true nature.

Figure 6. MsMpEng.exe metadata.
Conclusion
LevelBlue Labs has provided an overview on an ongoing crypto mining campaign that caught our eye due to the big number of loaders that have shown up during the month of June, as well as how staged the execution is for a simple malware like a miner. LevelBlue Labs will continue to monitor this campaign and include all the current and future IOCs in the pulse in Appendix B.
Associated indicators (IOCs)
The following technical indicators are associated with the reported intelligence. A list of indicators is also available in the OTX Pulse. Please note, the pulse may include other activities related but out of the scope of the report.
|
TYPE |
INDICATOR |
DESCRIPTION |
|
SHA256 |
fd5131645025e199caa142c12cef34b344437a0f58306f9b66c35d32618665ba |
ppercepciones anuales.xlsx |
|
SHA256 |
00ba928455d7d8a92e5aeed3146925086c2451501e63a0d8ee9b7cbaaf1007de |
CmRccService.exe |
|
SHA256 |
8f0dc8c5e23ee42209e222db5a8cf8ee6e5d10b5dde32db5937d4499deef0302 |
RegistryManager.exe |
|
SHA256 |
f77522d8476969ae13f8823b62646a9f2cec187e2d0e55298389b8ced60dd0c8 |
p.exe |
|
SHA256 |
ec4c48ac55139c6e4f94395aca253d54e9bbc864cc0741f8e051d31cd7545620 |
umxn.exe |
|
SHA256 |
c0dc67bfcefa5a74905f0d3a684e7c3214c5b5ca118e942d2f0cc2f53c78e06c |
oidz.exe |
|
SHA256 |
18493e0492eb276af746e50dee626f4d6a9b0880f063ebb77d8f3b475669bf65 |
Sample miner configuration |
|
DOMAIN |
2vkbjbpvqmoh[.]sh |
Malware and config server |
|
DOMAIN |
bekopgznpqe[.]is |
Malware and config server |
|
DOMAIN |
dpwdpqshxux[.]ru |
Unresolved domain |
Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK
The findings of this report are mapped to the following MITRE ATT&CK Matrix techniques:
- TA0001: Initial Access
- T1566: Phishing
- T1566.001: Spearphishing Attachment
- T1566: Phishing
- TA0002: Execution
- T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter
- T1059.001: PowerShell
- T1059.003: Windows Command Shell
- T1204: User Execution
- T1204.002: Malicious File
- T1569: System Services
- T1569.002: Service Execution
- T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter
- TA0003: Persistence
- T1543: Create or Modify System Process
- T1543.003: Windows Service
- T1543: Create or Modify System Process
- TA0004: Privilege Escalation
- T1543: Create or Modify System Process
- T1543.003: Windows Service
- T1543: Create or Modify System Process
- TA0005: Defense Evasion
- T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information
- T1027.002: Software Packing
- T1036: Masquerading
- T1036.004: Masquerade Task or Service
- T1562: Impair Defenses
- T1562.001: Disable or Modify Tools
- T1562.004: Disable or Modify System Firewall
- T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information
- TA0011: Command and Control
- T1102: Web Service
- T1102.003: One-Way Communication
- T1102: Web Service
- TA0040: Impact
- T1496: Resource Hijacking
- TA0042: Resource Development
- T1583: Acquire Infrastructure
- T1583.006: Domains
- T1583: Acquire Infrastructure
[1]EXE icon by Icons8; Cog icon by Icons8; XLS icon by Icons8
 [1]
[1]