On the My Subscription page, USM Anywhere displays the total data you have consumed for the month, the remaining data to be consumed, and the projected data you will consume based on your current usage. The service tier specified on your license determines the amount of data you're allowed to consume each month.

The Projected Data Consumption field is calculated using the following formula:
projectedMonthDataConsumption = currentMonthDataConsumption + (consumptionInLast24Hours * (hoursLeftInCurrentMonth/24))
Where:
- currentMonthDataConsumption = the total data consumed in the current month.
- consumptionInLast24Hours = the total data consumed over the past 24 hour period.
- hoursLeftInCurrentMonth = the number of hours remaining before the month ends.
For example, in a 30-day month, if at the end of the 15th day the instance has received 10 TB of data and the consumption in the last 24h is 0.48TB (20GB/h), the projected data consumption will be 10 TB + (0.48 TB * (360h / 24h)) = 17.2 TB.
The Projected Data Consumption field is crucial because it provides an estimate on how much data you will consume by the end of the month. This number should never exceed your allocated monthly usage. Exceeding the monthly limit automatically transitions your USM Anywhere into one of four Consumption Modes, determined by the degree to which you have exceeded your tier. More importantly, USM Anywhere's performance deteriorates. System process time increases, causing the sensor cache to fill up and the sensor to disconnect.
Note: See Understanding Your Data Consumption Status for more information on these Consumption Modes.
LevelBlue recommends that you monitor your projected data consumption early and constantly so that you can perform countermeasures when you're expected to exceed your monthly limit. You can reduce consumption by monitoring fewer networks, cutting down the number of data sources, or creating filtering rules to restrict data collection.
On the same My Subscription page, there is a chart that displays the data collected during the current period.

On the lower side of the page, there are three tables that show the breakdown of how much data is being processed by each data source, event names, and reporting device. You can use the Last 24 Hours filter for identifying data during the last hour, last 24 hours, last 7 days, last 30 days, or last 90 days. You can also configure your own period of time by clicking the Custom Range option. This option enables you to customize a range. When you click Custom Range, a calendar opens. You can choose the first and last day to delimit your search by clicking the days on the calendar or entering the days directly. Then select the hours, minutes, and seconds by clicking the specific box. Finally, select AM or PM.
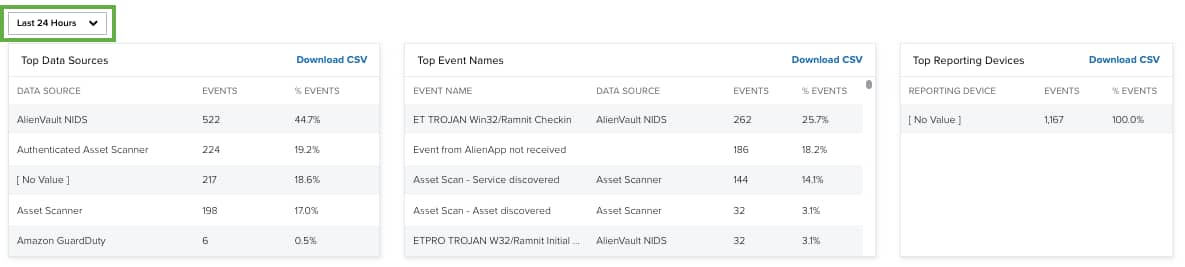
Click Download CSV to create a comma-separated value (CSV) file detailing the specific information of each table in a spreadsheet.
 Role Availability
Role Availability Read-Only
Read-Only
 Feedback
Feedback