| Applies to Product: |
|
|
Many external NetFlow sources (such as routers and switches) have NetFlow capabilities already defined in their operating firmware and usually require only some minimal configuration to enable it. NetFlow collection is entirely dependent upon having visibility to traffic traversing the network, which means the routers and switches that traffic flows over. There are two ways to acquire this, with both options supported by LevelBlueUSM Appliance:
- Method 1: A network device is configured with a SPAN/Mirror port to clone all traffic to a single port, which is attached to an existing USM Appliance Sensor. The USM Appliance Sensor, connected to the SPAN port, generates NetFlow data from the observed network traffic.
- Method 2: Network devices are configured to generate NetFlow data, and then transmit it directly to USM Appliance Server (through a pseudo or "dummy" configured USM Appliance sensor). NetFlow data is sent from the NetFlow source to the dummy sensor, which transmits the NetFlow data to the USM Appliance Server.
After configuring the USM Appliance sensor, configure network devices to send NetFlow data to the USM Appliance dummy sensor. Use the same port to send NetFlow data as configured for the dummy sensor. This task is vendor-specific. Consult your network device vendor documentation for instructions on how to configure NetFlow on a network device.
These two options are not mutually exclusive, so USM Appliance deployments can incorporate both methods of NetFlow data collection and generation.
Important: Be aware that when you enable NetFlow collection in USM Appliance, the flow data is kept in the file system consuming space. By default, USM Appliance stores flows for 45 days in /var/cache/nfdump/flows. For more information, see Back Up and Restore NetFlow Data
To capture NetFlow traffic information from a spanned or mirrored port, you can connect an existing USM Appliance Sensor to generate NetFlow data from the network traffic source. By default, NetFlow is disabled on USM Appliance Sensors (except for USM Appliance All-in-One), so you need to first activate and configure NetFlow collection and generation on the sensor. NetFlow collection is configured on a per-sensor basis, from the USM Appliance Sensor configuration screen:
To enable NetFlow collection from an Existing USM Appliance Sensor
- Go to Configuration > Deployment.
-
Select the Components > Sensors tab.
-
Click the IP Address of the sensor you want to configure to collect NetFlow source traffic information and generate NetFlow data to send to USM Appliance Server.
USM Appliance displays the main sensor configuration screen, with the NetFlow Collection Configuration detail appearing at the very bottom.
There are three primary configuration options, all of which may safely be left with their default values:
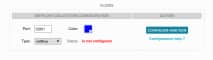
- Port — This is the port on which the USM Appliance Sensor will transmit NetFlow data back to the USM Appliance Server. Each sensor must transmit on a unique port number. A suitable default port number that you can use will appear in this text box. You can use this port unless you have a specific operational reason to choose another port, perhaps, because your network has a specific port range assigned for administrative traffic ACLs.
- Type — This is the type of NetFlow data that the sensor will receive from external sources. If you are only using the USM Appliance Sensor to generate NetFlow data, you can keep the default setting.
- Color — A color value to visually identify flows collected from this sensor in the Flows analysis section of the USM Appliance Web UI Environment > NetFlow web page.
Note: Generally acceptable options are NetFlow and sFlow. In short, NetFlow provides IP flow aggregation, while sFlow provides sampled network data. Your selection of NetFlow type depends on the network device used, and its configuration. If you use Cisco or Enterasys network devices, select NetFlow. For other vendors, select sFlow.
-
Once you have chosen appropriate values (or kept their default settings), click Configure and Run to activate NetFlow collection/generation from this sensor.
The configuration section is updated to indicate that NetFlow collection for the USM Appliance Sensor is now configured.
To Enable NetFlow Generation on External Sensors
If you have added any external sensors to a USM Appliance All-in-One or other standard server installation, you need to perform one extra step to configure the internal NetFlow generation on those sensors.
-
Log into the external sensor using SSH and the credentials needed to gain access to the sensor.
-
From the Setup menu, select the Configure Sensor > Enable NetFlow Generator option.
-
Set the Enable NetFlow Generator option to yes.
-
Click OK.
You are now prompted to specify the Remote Collector Port. This is the port on which the Sensor will transmit NetFlow data back to the USM Appliance Server.
-
Specify the same port number as you selected in Step 3 of the previous procedure, “Enabling NetFlow Collection from an Existing USM Appliance Sensor (Method 1) ”.
-
Click OK.
-
Return to the main Setup menu and select Apply all Changes.
-
Exit the Setup menu and log off the sensor.
Network devices that directly support the collection, generation, and transmission of NetFlow data (or data from the variant sFlow) may also be configured as a source of NetFlow traffic information within LevelBlueUSM Appliance.
To capture NetFlow data generated by these devices, you need to create a "dummy" sensor in USM Appliance and then configure the device to transmit the NetFlow or sFlow information to the USM Appliance Server.
Note: Configuring a USM Appliance "dummy" sensor just sets up a "listener" interface for the NetFlow source to send NetFlow data directly to the USM Appliance Server.
To enable NetFlow collection from a new USM Appliancedummy sensor
- Go to Configuration > Deployment.
-
Select the Components > Sensors tab.
-
Click New to create a new sensor.
USM Appliance opens the sensor configuration page.
-
Specify a name and description to identify the new sensor and the IP Address of the network device sending NetFlow data to USM Appliance.
-
Click Save.
USM Appliance return to the Components > Sensors page, now listing the new sensor you just created.
-
Select the new sensor you just created, and click Modify.
-
Scroll down the sensor configuration page to the Services section and disable all services.
This step is not essential, but it prevents this "dummy" sensor from showing up as an available sensor under several configuration sub-menus. When displaying a list of sensors in the USM Appliance web UI, the dummy sensor will show up in the sensor list, but will display the status as down, as the sensor will not respond to API requests.
-
Scroll further down the sensor configuration page to the Flows section.
There are three primary configuration options, all of which may safely be left with their default values:
- Port — This is the port on which the USM Appliance Sensor will transmit NetFlow data back to the USM Appliance Server. Each sensor must transmit on a unique port number. A suitable default port number that you can use will appear in this text box. You can use this port unless you have a specific operational reason to choose another port, perhaps, because your network has a specific port range assigned for administrative traffic ACLs.
- Type — This is the type of NetFlow data that the sensor will receive from external sources. If you are only using the USM Appliance Sensor to generate NetFlow data, you can keep the default setting.
Note: Generally acceptable options are NetFlow and sFlow. Your selection of NetFlow type depends on the network device used, and its configuration. If you use Cisco or Enterasys network devices, select NetFlow. For other vendors, select sFlow.
- Color — A color value to visually identify flows collected from this sensor in the Flows analysis section of the USM Appliance Web UI Environment > NetFlow web page.
-
Once you have chosen appropriate flow configuration values (or kept their default settings), click the Configure and Run button to configure and activate NetFlow data collection from this sensor.
USM Appliance displays a dialog box prompting you to confirm configuration changes to the new sensor.
-
Click Yes.
USM Appliance applies the required sensor changes and then returns to the listing of configured sensors.
Note: After making sensor configuration changes to enable NetFlow capture, make sure that you also configure your network device to match settings specified in the sensor configuration detail. Refer to vendor documentation available for your network devices for any specific configuration required to enable or configure NetFlow data collection and generation.
After configuring USM Appliance Sensors and network devices, you can verify USM Appliance collection of NetFlow data.
Note: Because NetFlow data collection requires capture of live network traffic, you should wait a short period (15 to 30 minutes) to allow USM Appliance time to collect a reasonable sampling of data from your network.
-
Select the Environment > NetFlow menu option.
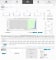
USM Appliance displays the following page.
-
In the middle section of the NetFlow Detail page, you can toggle the selection of statistics and graphs for data from different NetFlow sources. You can focus the display on individual flow sources by selecting a particular NetFlow source in the bottom portion of the Detail page, labelled NetFlow Processing.
-
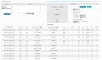
You can further qualify NetFlow data by clicking on one of the predefined processing options, such as List Last 500 Sessions or Top 10 Src Ports, as well as selecting options from the Options section.
The following display shows a sample of results for List Last 500 Sessions.
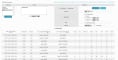
You can define more specific selection criteria for NetFlow data displays in the Filter box, for example: ip x.x.x.x
The main NetFlow web page provides three different tab selections, Details (the default), Overview, and Graph. The graphs displayed on the Details page provide a quick visual confirmation that NetFlow data is being captured. The colors used to plot the flow graphs are the colors assigned to each sensor as part of their configuration.
The Detail page also provides statistics for flows, packets, and traffic. Statistics are displayed separately for TCP, UDP, ICMP, and other protocols. The NetFlow page provides separate graphics and statistics for each NetFlow data source. In addition, you can adjust the time frame for a graph, by moving the sliders in the time line, or specifying a time range from the Display drop-down menu.
You can find more filter examples at http://biot.com/capstats/bpf.html.







 Feedback
Feedback