 Role Availability Role Availability
|
 Read-Only Read-Only
|
 Investigator Investigator |
 Analyst Analyst
|
 Manager Manager
|
Syslog is a message-logging standard supported by most devices and operating systems. USM Anywhere uses Syslog-ng, which supports IETF-syslog protocol, as described in RFC 5424 and RFC 5426; and BSD-syslog-formatted messages, as described in RFC 3164. While RFC 5424 and RFC 3164 define the format and rules for each data element within the syslog header, there can be a great deal of variance in the message content received from your data sources. Although Syslog-ng fixes some missing or incorrect headers, USM Anywhere doesn’t support syslog-formatted messages other than the ones previously mentioned.
Note: You can send syslog messages to USM Anywhere directly from the data source or use log-forwarding software such as Splunk or Loggly. USM Anywhere accepts most log-forwarding software that doesn't alter the raw log messages.
The USM Anywhere Sensors use the syslog server app to collect syslog messages for processing. The USM Anywhere Sensor passively listens on the syslog ports.
The following tables list the ports that require the syslog server app for the RFC 3164 and RFC 5424 protocols.
| Protocol | Port | BSD – Syslog Protocol Support |
|---|---|---|
|
UDP |
514 |
USM Anywhere collects data through syslog over UDP on port 514 by default. |
|
TCP |
601 |
USM Anywhere collects data through syslog over TCP on port 601 by default. |
|
TLS/TCP |
6514 |
USM Anywhere collects Transport Layer Security (TLS)-encrypted data through syslog over TCP on port 6514 by default. Important: USM Anywhere requires the use of the TLS 1.2 protocol to ensure security. |
| Protocol | Port | IETF – Syslog Protocol Support |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 602 | USM Anywhere collects data through syslog over TCP on port 602 by default. |
| TLS | 6515 |
USM Anywhere collects data through syslog over TLS on port 6515 by default. Important: USM Anywhere requires the use of the TLS 1.2 protocol to ensure security. |
Important: Make sure that the required ports are open for these protocols within your security groups and firewalls.
Configure Syslog on Your Data Sources
For each of the data sources in your network where you want to collect syslog data, you must forward the logs to a USM Anywhere Sensor. Use the following configuration information to use rsyslog Open source software utility implementing the syslog protocol to forward log messages to/from UNIX and Linux-based computers operating in a TCP/IP network environment. to collect and send syslog to your USM Anywhere Sensor. Many third-party systems and devices support other methods for sending syslog messages. Go to the specific BlueApp in USM Anywhere for instructions about syslog forwarding.
Note: The *.* configuration enables you to forward all syslog messages. However, LevelBlue strongly recommends that you use any of the rsyslog filtering capabilities to forward only the logs that need to be monitored by USM Anywhere.
Important: You have to use the following syntax in the /etc/rsyslog.conf with older version of rsyslog:
*.* @remote_server:port
Standard Syslog over UDP
To configure syslog over UDP, you need to configure rsyslog on your data source to forward the logs to your USM Anywhere Sensor over the UDP port (the default is 514).
*.* action(type="omfwd" target="<IP>" port="514" protocol="udp" action.resumeRetryCount="100" queue.type="linkedList" queue.size="10000") # send (all) messages - Forward to the USM Anywhere Sensor IP address
Where <IP> is the IP address for the USM Anywhere Sensor.
Standard Syslog over TCP
To configure syslog over TCP, you need to configure rsyslog on your data source to forward the logs to your USM Anywhere Sensor over the TCP port (default 601).
*.* action(type="omfwd" target="<IP>" port="601" protocol="tcp" action.resumeRetryCount="100" queue.type="linkedList" queue.size="10000") # send (all) messages - Forward to the USM Anywhere Sensor IP address
Where <IP> is the IP address for the USM Anywhere Sensor.
TLS-Encrypted Syslog over TCP
If you want to enable encrypted syslog communications between a host and the USM Anywhere Sensor to comply with your organization's security policies that require encryption of log data in transit, you can configure syslog TLS/TCP forwarding. TLS uses certificates to encrypt the communication between a client (the data source) and server (the USM Anywhere Sensor).
To configure syslog for TLS over TCP, you need to configure rsyslog on your data source to use TLS encryption and forward the logs to your USM Anywhere Sensor over the default port (6514 or 6515). The following configuration information is tested on Ubuntu 16.04 using rsyslog 8. For Red Hat Linux distributions, use rpm or yum in place of apt-get. For other systems supporting rsyslog TLS configuration, you can extrapolate from this information.
Note: For devices such as Trend Micro and Palo Alto Networks, LevelBlue requires you to upload your own certificates to both the device and the USM Anywhere Sensor. See Upload Your Own Certificate for more information.
The network stream driver implements a TLS-protected transport through the GnuTLS library.
sudo apt-get install rsyslog-gnutls
You can download the library from the GnuTLS site: https://gnutls.org/download.html.
USM Anywhere provides a digital certificate that enables the SSL Protocol used for transmitting private documents through the Internet. SSL works by using a public key to encrypt data that's transferred over the SSL connection. See also transport layer security. operation and the crypto keys used to secure the connection. This certificate is automatically renewed or updated with no maintenance requirement on your part.
Note: LevelBlue recommends you follow these steps to configure remote forwarders.
To download and install the certificate
- In USM Anywhere, go to Data Sources > Sensors.
- Click the Sensor Apps tab.
- In the left navigation, select Syslog Server.
-
Select the sensor where you want to forward the logs.
-
Download the certificate by clicking the Download LevelBlue CA Certificate link.
- Copy the certificate file to the client system.
- Configure the rsyslog service. See Configure the rsyslog Service for more information.
You can upload your own TLS certificate and deploy it on the syslog server app through port 6514 or 6515. If you choose to generate and upload your own TLS certificate, you must provide the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate, the Server Certificate (signed by the root certificate authority, not an intermediate certificate), and the Server Private Key. USM Anywhere supports intermediate certificates for both self-signed or not self-signed.
To upload your own TLS certificate
- In USM Anywhere, go to Data Sources > Sensors.
- Click the Sensor Apps tab.
- In the left navigation, select Syslog Server.
- Under the Syslog Server header, click the Settings tab.
-
Paste the raw text of your PEM files to each of the fields individually.
- Both the CA Certificate and Server Certificate must contain the PEM delimited -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- header and -----END CERTIFICATE----- footer.
- The Server Private Key must be formatted in Public-Key Cryptography Standards (PKCS) #8 standard syntax and contain the PEM delimited -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- header and -----END PRIVATE KEY----- footer.
- If you want to use intermediate certificates, paste this text:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
(Your Intermediate2 certificate if exists)
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
(Your Intermediate1 certificate if exists)
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
(Your Root certificate)
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
- If you don't want to use intermediate certificates, paste this text:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
(Your Root certificate)
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
- Click Save to deploy your custom certificates.
Warning: The full chain of certificates must be contained if you want to upload your own TLS certificate. This includes the root certificate.
After you have uploaded your certificates, you can confirm that they have been saved by clicking the Status tab of the Syslog Server page. The Status for Uploaded TLS Certificate will now display the message Uploaded Successfully, and the Health displays the green checkmark icon.
Thereafter, if you want to use the default TLS certificates instead, you need to remove the custom certificates first.
To remove your custom certificates and use the default TLS certificates
- In USM Anywhere, go to Data Sources > Sensors.
- Click the Sensor Apps tab.
- In the left navigation, select Syslog Server.
- Under the Syslog Server header, click the Settings tab.
- Delete the text in the PEM certificate fields and click Save.
- Under the Syslog Server header, click the Actions tab.
-
In the Regenerate LevelBlue TLS Certificates action row, click Run.
The Select Action window displays the Action Type as Syslog Server, and the App Action as Regenerate LevelBlue TLS Certificates.
- Click the Run button to regenerate the TLS certificates.
Edit the rsyslog configuration file to send logs to the USM Anywhere Sensor. The configuration file is located at /etc/rsyslog.conf by default.
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /PATH/TO/CERTIFICATE
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
$ActionSendStreamDriverMode 1
$ActionSendStreamDriverAuthMode anon
*.* action(type="omfwd" target="<IP>" port="6514" protocol="tcp" action.resumeRetryCount="100" queue.type="linkedList" queue.size="10000") # send (all) messages - Forward to the USM Anywhere Sensor IP address
Where <IP> is the IP address for the USM Anywhere Sensor.
You must restart the rsyslog service for the configuration change to take effect.
sudo service rsyslog restart
Note: When redeploying a sensor with TLS syslog encryption enabled, the new sensor will not maintain your previous encryption configuration. You must configure your TLS syslog encryption again for the redeployed sensor:
- If you have used the default sensor certificates, the redeployed sensor will have generated new certifications. Be sure to use the new sensor certifications when reconfiguring your TLS syslog encryption.
- If you have used your own TLS certificates you must reupload your PEM files again, but they can be the same PEM files you used originally.
Check the Syslog Collection Status
After you have configured the syslog forwarding policy on the required data sources, you can verify the log forwarding in USM Anywhere. When you select the sensor on the Syslog Server page, the Health column displays for each of the syslog protocols where the sensor has received a packet within the last 10 minutes.
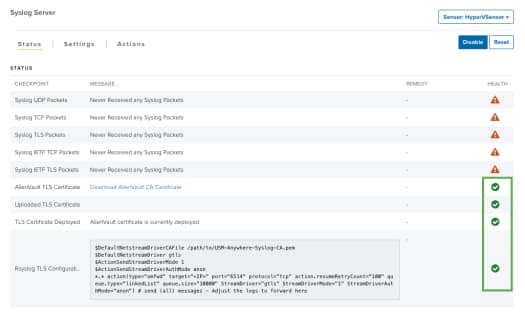
Scroll down to the Stats section to review more detailed information about the syslog activity on the sensor.
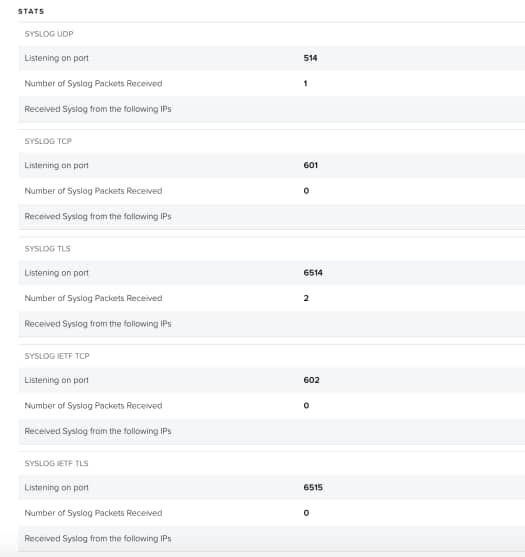
- Number of Syslog Packets Received: Number of packets received by the sensor since it has been up and running. (Restarting the sensor resets this counter.)
- Received Syslog from the following IPs: List of IP addresses forwarding logs to the sensor. There is a maximum of 100 IPs, and IPs not sending logs in the last 24 hours are discarded. (Restarting the sensor resets this list.)
Disable Syslog Collection on a USM Anywhere Sensor
The syslog server app is enabled for log collection by default for each deployed USM Anywhere Sensor. If you want to disable the app for a particular sensor, complete the following procedure.
To disable syslog data collection on a sensor
- In USM Anywhere, go to Data Sources > Sensors.
- Click the Sensor Apps tab.
- In the left navigation menu, click Syslog Server.
-
Select the sensor where you want to disable the app.

- Click Disable.
 Feedback
Feedback